Alexei Shulgin, born in 1963 in Moscow. Since mid 80’s e has been working in the fields of photography, media and contemporary arts. In the 90’s he was one of the pioneers of Net Art. His cyberpunk rock band, 386 DX has toured extensively all over the world. Alexei has participated in numerous exhibitions, media art and music festivals in Russia and internationally. He was teaching at Proarte Institute in St. Petersburg in 2000-2001 and performed as a guest teacher at a number of art schools in Europe and the US. Alexei has curated several exhibitions; in 2001-2004 he was a co-organizer of Readme software art festival (Moscow-Helsinki-Aarhus-Dortmund). He is a co-admin of Runme.org software art repository on the Internet. In 2004 he has co-founded Electroboutique gallery in Moscow. At present, he teaches at Rodchenko school of Photography and Media Art in Moscow. Alexei Shulgin lives and works in Moscow.[1]
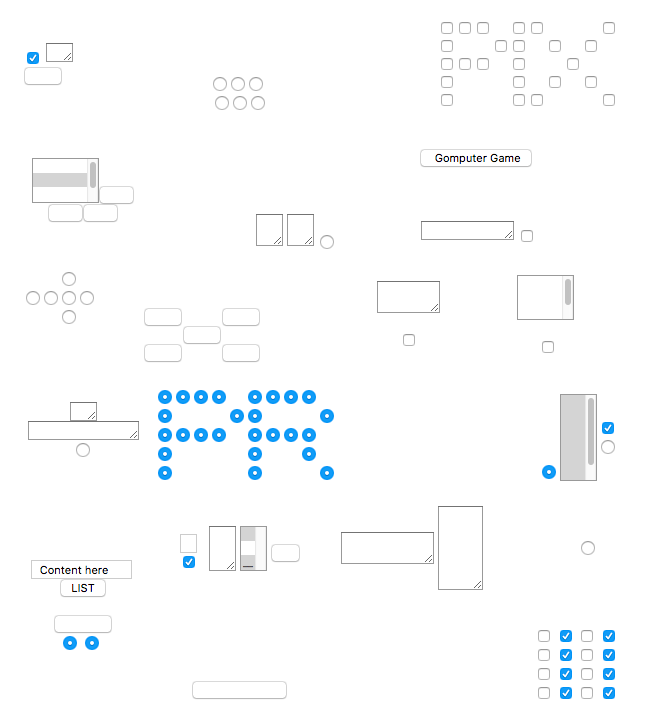
Particularly involved with software art and internet art, he is a part of the readme culture and uses code as a form of art. In 1997, he released his first interactive work, Form Art, in which only minimum factors are programmed in the form of HTML. Shulgin describes this page as a "formalistic" aesthetic art site - a play on words taking into account the clean composition as well as the tools of its creation. Navigating this site requires aimless click-throughs of blank boxes and links, which lead the viewer through 19 pages of "form art" animations. Behavioral expectations are subverted by frequently overriding default functionality of basic form elements such as radio buttons and list boxes.[2]
Many links on his site are now 404, selected online works:
- http://www.c3.hu/collection/form/ - Form Art, 1997
- http://www.easylife.org/netart/ - Introduction to net.art. 1999
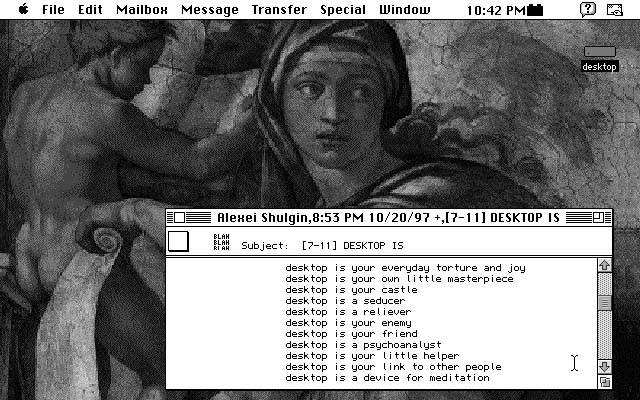
- http://www.easylife.org/desktop/ - First international desktop exhibition. 1997-98
- http://www.easylife.org/seefree/index.html - SeeFree©. 2003
- http://www.easylife.org/privatronics/index.html - Privatronics. 2003
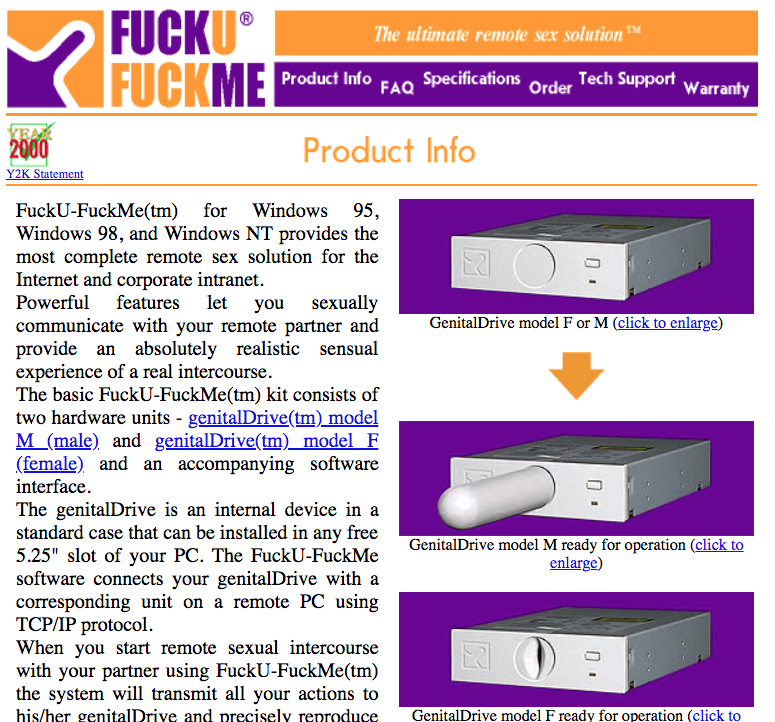
- http://www.easylife.org/fufme/ - FuckU-FuckMe. 1999
- http://www.easylife.org/this_morning/ - Desires are tearing me apart. 1997