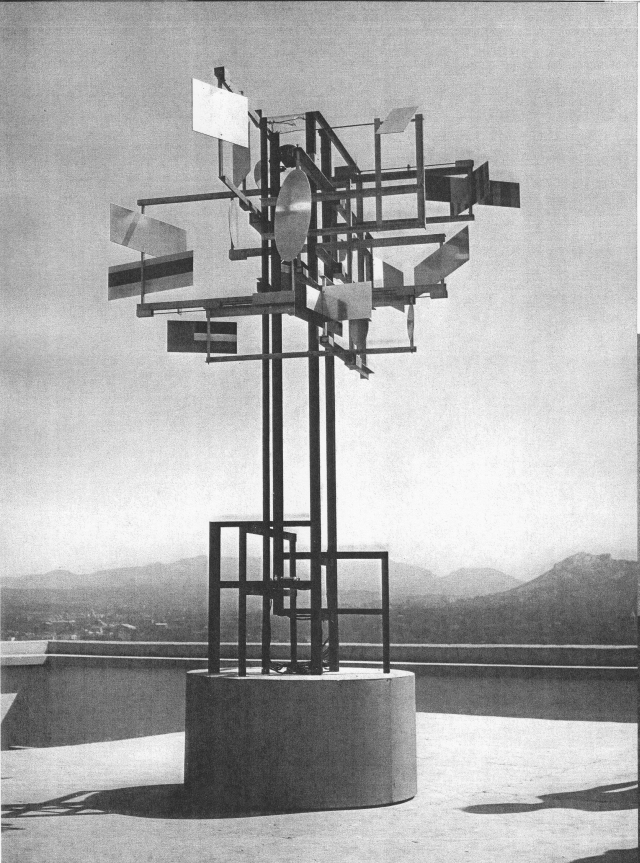
In 1956, Philips engineers helped Nicolas Schöffer create CYSP I, which employed an “electronic brain” connected to sensors that enabled the human-scale kinetic sculpture to respond to changes in sound, light intensity and colour, and movement, including that of the audience. The whole sculpture moves on four rollers and its sixteen polychrome plates, which pivot and spin at different rates depending on external stimulus. It premiered in a performance with the Maurice Bejart dance company, interacting with the dancers on the roof of Le Corbusier’s Cité Radieuse, accompanied by concrete music composed by Pierre Henry. This early responsive, robotic sculpture is perhaps the first work of art to explicitly incorporate the principles of cybernetics (CYSP is an acronym formed from the first two letters of the words cybernetic and spatiodynamic). It has had an extensive exhibition history and the sculpture survives in the artist’s estate.
The whole is set on a base mounted on four rollers, which contains the mechanism and the electronic brain. The plates are operated by small motors located under their axis. Photo-electric cells and a microphone built into the whole catch all the variations in the fields of color, light intensity and sound intensity. All these changes occasion reactions on the part of the sculpture consisting of combined travel and animation.
For example: it is excited by the color blue, which means that it moves forward, retreats or makes a quick turn, and makes its plates turn fast; it becomes calm with red, but at the same time it is excited by silence and calmed by noise. It is also excited in the dark and becomes calm en intense light.
Inasmuch as these phenomena are constantly variable, the reactions are likewise ever changing and unpredictable, which endows the mechanism with an almost organic life and sensitivity.